motion_sensor — Onboard Motion Sensor¶
motion_sensor The main functionality and functions of the module
- Description of onboard attitude sensor module:
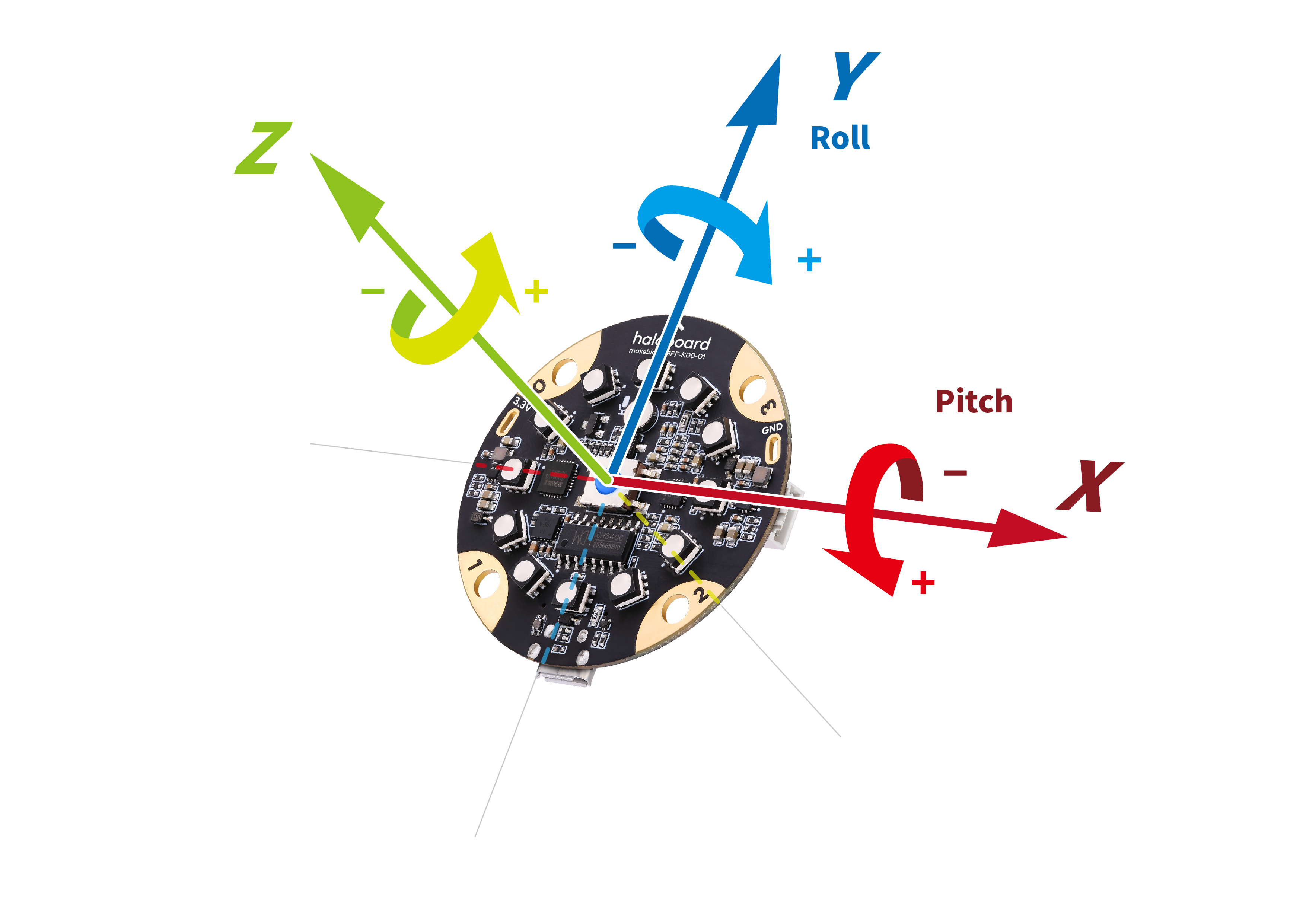
As shown in the figure above, the direction of roll and pitch is based on the right hand screw rule. Haloboard horizontal roll and pitch of 0 °
- roll - Scope: - 90 ° ~ 90 °
- pitch - Scope: -180° ~ 180°
Function¶
-
motion_sensor.get_roll()¶ Gets the roll angle of the attitude angle, and the range of returned data is -90 ~ 90.
-
motion_sensor.get_pitch()¶ Get the pitch angle of the attitude angle, and the data range returned is -180 ~ 180.
-
motion_sensor.get_yaw()¶ The yaw angle of the attitude angle is obtained, and the range of data returned is 0 ~ 360. Since there is no electronic compass, the yaw angle is actually just an integral of the z-axis angular velocity.It has accumulated errors.If you want to get real yaw angles, this API is not suitable.
-
motion_sensor.get_acceleration(axis)¶ For three axis acceleration value, the unit is m/s ^ 2, and parameters:
- axis - String type, x, y, z represents the axis defined by the haloboard.
-
motion_sensor.get_gyroscope(axis)¶ Get three shaft angular velocity value, the unit is ° / SEC, parameters:
- axis - String type, x, y, z represents the axis defined by the haloboard.
-
motion_sensor.get_rotation(axis)¶ Obtain the rotation angle of the haloboard on three axes, with the counterclockwise rotation as the positive direction, parameters:
- axis - String type, x, y, z represents the axis defined by the haloboard.
-
motion_sensor.reset_rotation(axis = "all")¶ The current angle of rotation around three axes is 0. The get_rotation() function will start from 0, parameter:
- axis - String type, x, y, z represents the axis defined by the haloboard, “all” represents all three axes and is the default value for this function.
-
motion_sensor.is_tilted_left()¶ Detect whether haloboard tilt to the left, threshold 15 °, the return value is a boolean value, “True” said haloboard tilt to the left, “False” said haloboard not tilt to the left.
-
motion_sensor.is_tilted_right()¶ Detect whether haloboard tilt to the right, threshold 15 °, the return value is a boolean value, “True” said haloboard tilt to the right, “False” said haloboard not tilt to the right.
-
motion_sensor.is_arrow_up()¶ Detect whether get arrow up state, threshold 15 °, the return value is a boolean value, which “True” arrow up, says “False” indicates no up arrow.
-
motion_sensor.is_arrow_down()¶ Detect whether get arrow down state, threshold 15 °, the return value is a boolean value, which “True” arrow down, says “False” indicates no down arrow.
-
motion_sensor.is_shaked()¶ Detect whether the haloboard is shaken, and the return value is boolean, where “True” means that the haloboard is shaken, and “False” means that the haloboard is not shaken.
-
motion_sensor.is_led_ring_up()¶ Detect whether the LED lamp ring is upwards and return a boolean value, where “True” means the lamp ring is upwards and “False” means the lamp ring is not upwards.
-
motion_sensor.is_led_ring_down()¶ Detect whether the LED lamp ring is downwards and return a boolean value, where “True” means the lamp ring is downwards and “False” means the lamp ring is not downwards.
-
motion_sensor.get_shake_strength()¶ If the haloboard is shaken, this function can obtain the strength of the shaking. The value range of the return value is 0 ~ 100. The larger the value is, the stronger the shaking will be.
Sample Code 1:¶
import haloboard
import time
while True:
acceleration_x = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_acceleration("x")
acceleration_y = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_acceleration("y")
acceleration_z = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_acceleration("z")
print("acceleration_x:", end = "")
print(acceleration_x, end = "")
print(" ,acceleration_y:", end = "")
print(acceleration_y, end = "")
print(" ,acceleration_z:", end = "")
print(acceleration_z)
time.sleep(0.05)
Sample Code 2:¶
import haloboard
import time
while True:
roll = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_roll()
pitch = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_pitch()
yaw = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_yaw()
print("roll:", end = "")
print(roll, end = "")
print(" ,pitch:", end = "")
print(pitch, end = "")
print(" ,yaw:", end = "")
print(yaw)
time.sleep(0.05)
Sample Code 3:¶
import haloboard
import time
while True:
gyroscope_x = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_gyroscope("x")
gyroscope_y = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_gyroscope("y")
gyroscope_z = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_gyroscope("z")
print("gyroscope_x:", end = "")
print(gyroscope_x, end = "")
print(" ,gyroscope_y:", end = "")
print(gyroscope_y, end = "")
print(" ,gyroscope_z:", end = "")
print(gyroscope_z)
time.sleep(0.05)
Sample Code 4:¶
import haloboard
import time
while True:
if haloboard.motion_sensor.is_tilted_left():
print("tilted_left")
if haloboard.motion_sensor.is_tilted_right():
print("tilted_right")
if haloboard.motion_sensor.is_arrow_up():
print("arrow_up")
if haloboard.motion_sensor.is_arrow_down():
print("arrow_down")
Sample Code 5:¶
import haloboard
import time
while True:
rotation_x = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_rotation("x")
rotation_y = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_rotation("y")
rotation_z = haloboard.motion_sensor.get_rotation("z")
print("rotation_x:", end = "")
print(rotation_x, end = "")
print(" ,rotation_y:", end = "")
print(rotation_y, end = "")
print(" ,rotation_z:", end = "")
print(rotation_z)
time.sleep(0.05)
Sample Code 6:¶
import haloboard
import time
while True:
if haloboard.motion_sensor.is_shaked():
print("shake_strength:", end = "")
print(haloboard.motion_sensor.get_shake_strength())
Sample Code 7:¶
import haloboard
import time
while True:
if haloboard.motion_sensor.is_led_ring_up():
print("led ring up")
if haloboard.motion_sensor.is_led_ring_down():
print("led ring down")
time.sleep(0.3)